How Tesla's Regenerative Braking Works

Braking is essential to the driving experience, but not all systems are created equal. A regenerative braking system (RBS) is the most significant difference people notice the first time they operate an electric vehicle.
Regen, as commonly referred to, makes it possible to drive a Tesla and never touch the brake pedal (along with some brake blending for slow speeds), not only reducing wear and tear on braking components but putting energy back into the battery. There are some estimates that regenerative braking can add 10 percent more range and extend the life of braking mechanisms by more than 50 percent.
What is Tesla's Regenerative Braking?
Unlike traditional brakes, which rely on friction to stop the wheels from turning, regenerative braking uses the vehicle's electric motor to create resistance to slow down the vehicle. In addition to slowing the vehicle down without the use of brakes, the motor running in reverse acts as a generator and captures the kinetic energy that would typically be lost as heat and converts it into electrical energy, thereby increasing your vehicle's range.
How to Activate Regen in a Tesla
In a Tesla, the regenerative braking system is activated by lifting your foot off the accelerator. The more you ease off the accelerator, the stronger the braking force and the more energy is captured.
Tesla's Power Meter (Regen bar)

All Teslas feature a power meter either in the instrument cluster (Model S and X) or the center screen (Model 3 and Y) that displays the amount of energy being captured through regenerative braking, or the amount of energy being used by accelerating the vehicle.
The center of the line is considered neutral. Anything to the left of the center point means energy is being captured, while anything to the right means that energy is being used.
The further the line grows to the left, the greater the amount of regenerative braking is taking place, and the more it moves to the right, the greater the amount of power is being used.
The regenerative braking line is green, while the power line is black (or white when in dark mode). You may occasionally also see a gray line on the left side. This will appear if the vehicle has the 'Apply Brakes When Regenerative Braking Is Limited' feature turned on. This feature introduces a consistent braking experience when lifting your foot off the accelerator pedal when regenerative braking is limited.
You may also see the gray line appear on the left side of the power meter if the vehicle is in Autopilot. This helps the driver understand when the vehicle is using regenerative braking or physical brakes to slow down.
How Does Regenerative Braking Work?
모든 Tesla 차량�—� �'재된 회생 제동 기술�—� 대해 알아보세�"!
— Tesla Korea (@tesla_korea) August 30, 2024
인벤토리 주문하기?https://t.co/mgl0rpgyOe pic.twitter.com/xT5FUSVKGO
Without getting too deep into Physics, kinetic energy is energy in motion. Therefore, anytime a car slows down, the kinetic energy that is produced has to go somewhere. With traditional brakes, that is heat from abrasion generated from the brake pads squeezing the rotors. But this energy can be used in a different way. In the words of a Tesla engineer, "kinetic energy stored in a moving vehicle is related to the mass and speed of the vehicle by the equation E = ½mv²."
You can see this equation play out every time you drive your Tesla by looking at the vehicle's power meter.
The motor controller manages the torque of the motor. This action helps with both driving and regenerative braking. The position of the accelerator pedal tells the motor controller how much torque is needed. The motor controller then changes this into a voltage or current that produces the correct torque. The rotating force can be positive or negative. When it is negative, it means the vehicle is slowing down, and energy is returned to the battery.
Regenerative Braking Explained
Regenerative Braking Extends the Life of Your Brakes
One of the benefits of regenerative braking is that it can help to lengthen the life of your brakes. Regenerative braking slows the car reducing the work of your traditional braking system. In fact, Tesla estimates that their cars experience 50 percent less brake wear than conventional gasoline cars. Elon Musk predicted that Tesla's Semi would have brake pads that would "literally last forever" because the regenerative system would save those pieces from being used extensively.
It's estimated that regenerative braking captures up to 70 percent of the kinetic energy usually lost during braking and is put back into the battery. As described above, that energy can then extend the range between needing to charge.
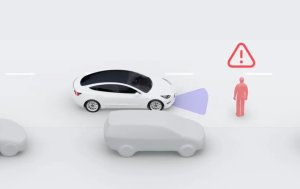
Does Regenerative Braking Activate Your Brake Lights?
During regenerative braking, Tesla will still activate the brake lights when the vehicle is slowing down, even if the brakes aren't being used at all. Tesla determines whether to turn on your brake lights based on your vehicle's rate of deceleration. If you're unsure if your brake lights are on, look at your Tesla screen, the car in the display shows the brake lights lit up when the brake lights are activated.
Levels of Regenerative Braking
It's important to note that regenerative braking cannot be turned off. There are two regenerative braking modes for 2020 and older models — low and standard. Tesla recommends that you use standard to maximize your vehicle's range. At some point in 2020, that choice was taken away, presumably to use all the benefits of regenerative braking all the time. However, there were some concerns, as regenerative braking can slow down the car rapidly; therefore limiting traction, the vehicle could slide. Tesla has this warning on its website: In snowy or icy conditions, Model S may experience loss of traction during regenerative braking.
Tire Configuration
The company also notes that installing winter tires may temporarily reduce regen. But the vehicle's systems are constantly recalibrating, so the feel of the vehicle will return to what the driver is used to after a few miles or trips.
You can speed up the calibration process by selecting the type of tires your vehicle is using. To select the type of tires your vehicle is using navigate to Controls > Service > Wheel & Tire Configuration > Tires and choose the appropriate tire type.
Regenerative Braking Limited or Reduced
Regenerative braking is not available or can be limited during certain conditions. If this happens, you may see a dotted line in the vehicle's power meter. If the battery is fully charged, there is nowhere for the kinetic energy to go. Consequently, regen won't work. It also has limited usage during cold weather due to a cold battery. In these cases, you can choose to activate 'Apply Brakes When Regenerative Braking Is Limited' to provide a consistent slow down experience. Tesla stated, "Your car can now automatically apply regular brakes for consistent deceleration when regenerative braking is limited due to battery temperature or state of charge." But the company did leave this as a preference, and the option can be turned off. You can activate it under Controls > Pedals & Steering.
Stopping Modes
Regenerative braking works best at certain speeds, if you're traveling too slow, regenerative braking may be limited or not available at all.
In a Tesla, your vehicle will use regenerative braking whenever you lift your foot off the accelerator pedal. However, if you're using Tesla's 'Hold' stopping mode, which allows you to drive with a single pedal most of the time, the vehicle will automatically blend in the vehicle's brakes when traveling 4 MPH (6.5 KPH) or slower.
If you're using Tesla's 'Creep' or 'Roll' stopping modes, the vehicle will never apply the brakes when lifting your foot off the accelerate, which means the vehicle will continue to roll at slow speeds when regenerative braking is no longer effect.
A Brief History of Regenerative Braking
Tesla used regenerative braking in its first car — The Roadster, in 2008. A year later, the same mechanics of the system were implemented in Formula 1. It is called KERS, which stands for Kinetic Energy Recovery System. It provides such a horsepower boost that it was banned for a season before being regulated the following year. However, this advanced system dates back to the late 1800s.
The Sprague Electric Railway and Motor Company is the earliest known use of the technology in 1886. General Electric used regen in 1936 in its locomotives, and Oerlikon, a Swiss company utilized some components of the system in its gyrobus. The Amitron, a concept electric car created by the American Motor Car Company included regenerative braking in its designs. Toyota introduced the technology to its brand with the Prius Hybrid in 1997 and GM's EV1 had regen when the company sent the cars to the crusher.
Regenerative braking is now a staple of the electric vehicle experience, not only reducing maintenance costs but also improving the vehicle's range and letting drivers accelerate and slow down with a single pedal.
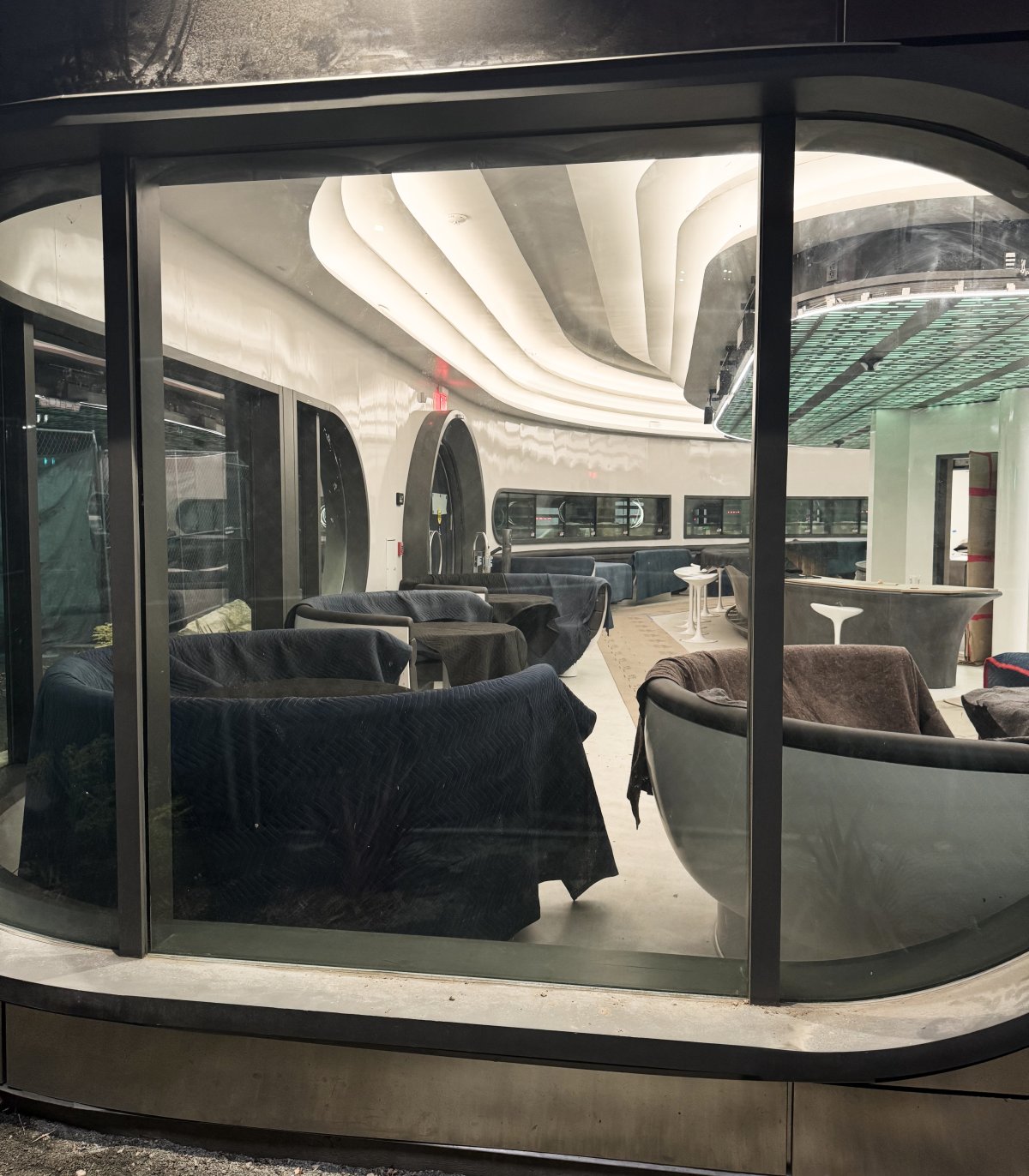


















![Exclusive: A Look Inside the Tesla Diner [PHOTOS]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/img/containers/article_images/2025/diner-seats.jpg/b0b4cb51b80d1f29298c9ca6b9ad2ae8/diner-seats.jpg)


_300w.png)