Tesla Holiday Update Wishlist - Charging & Safety Edition
As December approaches, Tesla’s highly anticipated Holiday update draws closer. Each year, this eagerly awaited software release transforms Tesla vehicles with new features and festive flair. If you’re not familiar with Tesla’s holiday updates, take a look at what Tesla has launched in the Holiday update the past few years.
While leaked features like Blind Spot Monitoring While Parked hint at thoughtful improvements, the real magic lies in the unexpected. From potential features such as the Apple Watch app to a smart assistant, the possibilities are endless.
For this chapter in our series, we’re dreaming up ways Tesla could improve the charging experience and even add some additional safety features. So let’s take a look.
Destination State of Charge
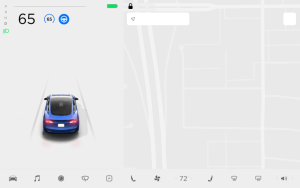
Today, navigating to a destination is pretty straightforward on your Tesla. Your vehicle will automatically let you know when and where to charge, as well as for how long. However, you’ll likely arrive at your destination at a low state of charge.
Being able to set your destination state of charge would be an absolute game-changer for ease of road-tripping. After all, the best EV to road trip in is a Tesla due to the Supercharger network. It looks like Tesla may be listening. Last week, Tesla updated their app and hinted at such a feature coming to the Tesla app. A Christmas present, maybe?
Battery Precondition Options
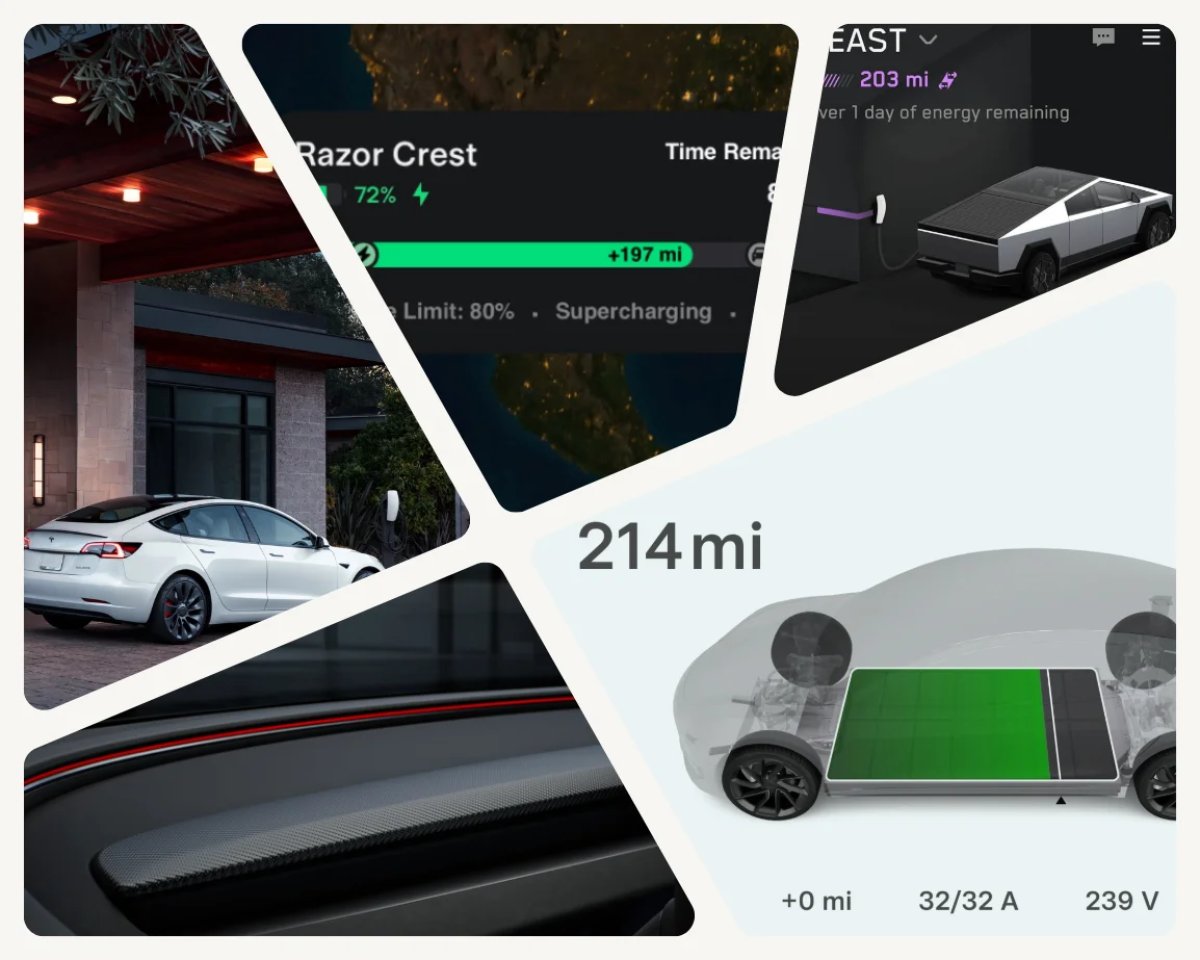
While Tesla automatically preconditions your battery when needed for fast charging, there are various situations where manually preconditioning the battery would be beneficial.
Currently, there is no way to precondition for third-party chargers unless you “navigate” to a nearby Supercharger. If you need to navigate to a Supercharger that’s close by, the short distance between your location and the Supercharger will also not allow enough time to warm up the battery, causing slower charging times.
In Europe, you can navigate to and precondition for Qualified Third Party Chargers, but not for unlabelled ones.
Live Activities
While we already mentioned Live Activities in the Tesla app wishlist, they’d be especially useful while Supercharging. Live Activities are useful for short-term information you want to monitor, especially if it changes often — which makes them perfect for Supercharging, especially if you want to avoid idle fees.
Vehicle-to-Load / Vehicle-to-Home Functionality
The Cybertruck introduced Tesla Power Share, Tesla’s name for Vehicle-to-Home functionality (V2H). V2H allows an EV to supply power directly to a home. By leveraging the vehicle’s battery, V2H can provide backup power during outages and reduce energy costs by using stored energy during peak rates.
Tesla Power Share integrates seamlessly with Tesla Energy products and the Tesla app. We’d love to see this functionality across the entire Tesla lineup. Recently a third party demonstrated that bidirectional charging does work on current Tesla vehicles – namely on a 2022 Model Y.
Adaptive Headlights for North America
While Europe and China have had access to the Adaptive Headlights since earlier this year, North America is still waiting. The good news is that Lars Moravy, VP of Vehicle Engineering, said that these are on their way soon.
Blind Spot Indication with Ambient Lighting
Both the 2024 Highland Model 3 Refresh and the Cybertruck already have ambient lighting features, but they don’t currently offer a practical purpose besides some eye candy. So why not integrate that ambient lighting into the Blindspot Warning system so that the left or right side of the vehicle lights up when there’s a vehicle in your blind spot? Currently, only a simple red dot lights up in the front speaker grill, and the on-screen camera will also appear with a red border when signaling.
Having the ambient lighting change colors when a vehicle is in your blind spot would be a cool use of the technology, especially since the Model Y Juniper Refresh and Models S and X are supposed to get ambient lighting as well.
Tesla’s Holiday update is expected to arrive with update 2024.44.25 in just a few short weeks. We’ll have extensive coverage of its features when it finally arrives, but in the meantime, be sure to check out our other wishlist articles:
Wishlist 1 - Tesla App Edition
Wishlist 2 - Tesla Maps & Autopilot Edition
Wishlist 3 - Tesla Entertainment Edition
Wishlist 4 - Tesla Charging & Safety Edition













![Tesla’s Missing Voice: Why a PR Team Matters More Than Ever [Opinion]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/img/containers/article_images/multiple-models/group_93.jpg/4e1056961f0480c7b9eff43dd2ec288e/group_93.jpg)












![Elon talks about Twitter and job cuts at Bloomberg forum [video]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/images/news/2022/elon-musk-qatar-forum_300w.jpg)